WSIReader¶
tiatoolbox.wsicore.wsireader.WSIReader
- class WSIReader(input_img, mpp=None, power=None)[source]¶
Base whole slide image (WSI) reader class.
This class defines functions for reading pixel data and metadata from whole slide image (WSI) files.
- input_path¶
Input path to WSI file.
- Type:
Path
- Parameters:
input_img (str,
Path,ndarrayorWSIReader) – Input path to WSI.mpp (
tupleorlistorNone, optional) – The MPP of the WSI. If not provided, the MPP is approximated from the objective power.power (
floatorNone, optional) – The objective power of the WSI. If not provided, the power is approximated from the MPP.
Initialize
WSIReader.Methods
Converts resolution value between different units.
Find optimal parameters for reading a rect at a given resolution.
Return an appropriate
WSIReaderobject.Read a region of the whole slide image within given bounds.
Read a region of the whole slide image at a location and size.
Read a region of the whole slide image (OpenSlide format args).
Generate image tiles from whole slide images.
Return the size of WSI at requested resolution.
Read the whole slide image thumbnail (1.25x by default).
Create a tissue mask and wrap it in a VirtualWSIReader.
Verify that an input image is supported.
Attributes
WSI metadata property.
- convert_resolution_units(input_res, input_unit, output_unit=None)[source]¶
Converts resolution value between different units.
This function accepts a resolution and its units in the input and converts it to all other units (‘mpp’, ‘power’, ‘baseline’). To achieve resolution in ‘mpp’ and ‘power’ units in the output, WSI metadata should contain mpp and objective_power information, respectively.
- Parameters:
input_res (Resolution) – the resolution which we want to convert to the other units.
input_unit (Units) – The unit of the input resolution (input_res). Acceptable input_units are ‘mpp’, ‘power’, ‘baseline’, and ‘level’. output_unit (str): the desired unit to which we want to convert the input_res. Acceptable values for output_unit are: ‘mpp’, ‘power’, and ‘baseline’. If output_unit is not provided, all the conversions to all the mentioned units will be returned in a dictionary.
output_unit (Units) – Units of scale, Supported units are: - microns per pixel (‘mpp’) - objective power (‘power’) - pyramid / resolution level (‘level’) - pixels per baseline pixel (“baseline”)
self (WSIReader)
- Returns:
Either a float which is the converted input_res to the desired output_unit or a dictionary containing the converted input_res to all acceptable units (‘mpp’, ‘power’, ‘baseline’). If there is not enough metadata to calculate a unit (like mpp or power), they will be set to None in the dictionary.
- Return type:
output_res (Resolution)
- find_read_rect_params(location, size, resolution, units, precision=3)[source]¶
Find optimal parameters for reading a rect at a given resolution.
Reading the image at full baseline resolution and re-sampling to the desired resolution would require a large amount of memory and be very slow. This function checks the other resolutions stored in the WSI’s pyramid of resolutions to find the lowest resolution (the smallest level) which is higher resolution (a larger level) than the requested output resolution.
In addition to finding this ‘optimal level’, the scale factor to apply after reading in order to obtain the desired resolution is found along with conversions of the location and size into level and baseline coordinates.
- Parameters:
location (IntPair) – Location in terms of the baseline image (level 0) resolution.
size (IntPair) – Desired output size in pixels (width, height) tuple.
resolution (Resolution) – Desired output resolution.
units (Units) – Units of scale, default = “level”. Supported units are: - microns per pixel (‘mpp’) - objective power (‘power’) - pyramid / resolution level (‘level’) - pixels per baseline pixel (“baseline”)
precision (int, optional) – Decimal places to use when finding optimal scale. See
find_optimal_level_and_downsample()for more.self (WSIReader)
- Returns:
Parameters for reading the requested region.
int- Optimal read level.
- Return type:
- property info: WSIMeta¶
WSI metadata property.
This property is cached and only generated on the first call.
- Returns:
An object containing normalized slide metadata.
- Return type:
- static open(input_img, mpp=None, power=None, **kwargs)[source]¶
Return an appropriate
WSIReaderobject.- Parameters:
input_img (str, Path,
numpy.ndarrayorWSIReader) – Input to create a WSI object from. Supported types of input are: str andPathwhich point to the location on the disk where image is stored,numpy.ndarrayin which the input image in the form of numpy array (HxWxC) is stored, orWSIReaderwhich is an already created tiatoolbox WSI handler. In the latter case, the function directly passes the input_imge to the output.mpp (tuple) – (x, y) tuple of the MPP in the units of the input image.
power (float) – Objective power of the input image.
kwargs (dict) – Key-word arguments.
- Returns:
An object with base
WSIReaderas base class.- Return type:
Examples
>>> from tiatoolbox.wsicore.wsireader import WSIReader >>> wsi = WSIReader.open(input_img="./sample.svs")
- read_bounds(bounds, resolution=0, units='level', interpolation='optimise', pad_mode='constant', pad_constant_values=0, coord_space='baseline', **kwargs)[source]¶
Read a region of the whole slide image within given bounds.
Bounds are in terms of the baseline image (level 0 / maximum resolution).
Reads can be performed at different resolutions by supplying a pair of arguments for the resolution and the units of resolution. If metadata does not specify mpp or objective_power then baseline units should be selected with resolution 1.0
The output image size may be different to the width and height of the bounds as the resolution will affect this. To read a region with a fixed output image size see
read_rect().- Parameters:
bounds (IntBounds) – By default, this is a tuple of (start_x, start_y, end_x, end_y) i.e. (left, top, right, bottom) of the region in baseline reference frame. However, with coord_space=”resolution”, the bound is expected to be at the requested resolution system.
resolution (Resolution) – Resolution at which to read the image, default = 0. Either a single number or a sequence of two numbers for x and y are valid. This value is in terms of the corresponding units. For example: resolution=0.5 and units=”mpp” will read the slide at 0.5 microns per-pixel, and resolution=3, units=”level” will read at level at pyramid level / resolution layer 3.
units (Units) – Units of resolution, default=”level”. Supported units are: microns per pixel (mpp), objective power (power), pyramid / resolution level (level), pixels per baseline pixel (baseline).
interpolation (str) – Method to use when resampling the output image. Possible values are “linear”, “cubic”, “lanczos”, “area”, and “optimise”. Defaults to ‘optimise’ which will use cubic interpolation for upscaling and area interpolation for downscaling to avoid moiré patterns.
pad_mode (str) – Method to use when padding at the edges of the image. Defaults to ‘constant’. See
numpy.pad()for available modes.pad_constant_values (int, tuple(int)) – Constant values to use when padding with constant pad mode. Passed to the
numpy.pad()constant_values argument. Default is 0.coord_space (str) – Defaults to “baseline”. This is a flag to indicate if the input bounds is in the baseline coordinate system (“baseline”) or is in the requested resolution system (“resolution”).
**kwargs (dict) – Extra key-word arguments for reader specific parameters. Currently only used by
VirtualWSIReader. See class docstrings for more information.self (WSIReader)
- Returns:
Array of size MxNx3 M=end_h-start_h, N=end_w-start_w
- Return type:
Examples
>>> from tiatoolbox.wsicore.wsireader import WSIReader >>> from matplotlib import pyplot as plt >>> wsi = WSIReader.open(input_img="./CMU-1.ndpi") >>> # Read a region at level 0 (baseline / full resolution) >>> bounds = [1000, 2000, 2000, 3000] >>> img = wsi.read_bounds(bounds) >>> plt.imshow(img) >>> # This could also be written more verbosely as follows >>> img = wsi.read_bounds( ... bounds, ... resolution=0, ... units="level", ... ) >>> plt.imshow(img)
Note: The field of view remains the same as resolution is varied when using
read_bounds().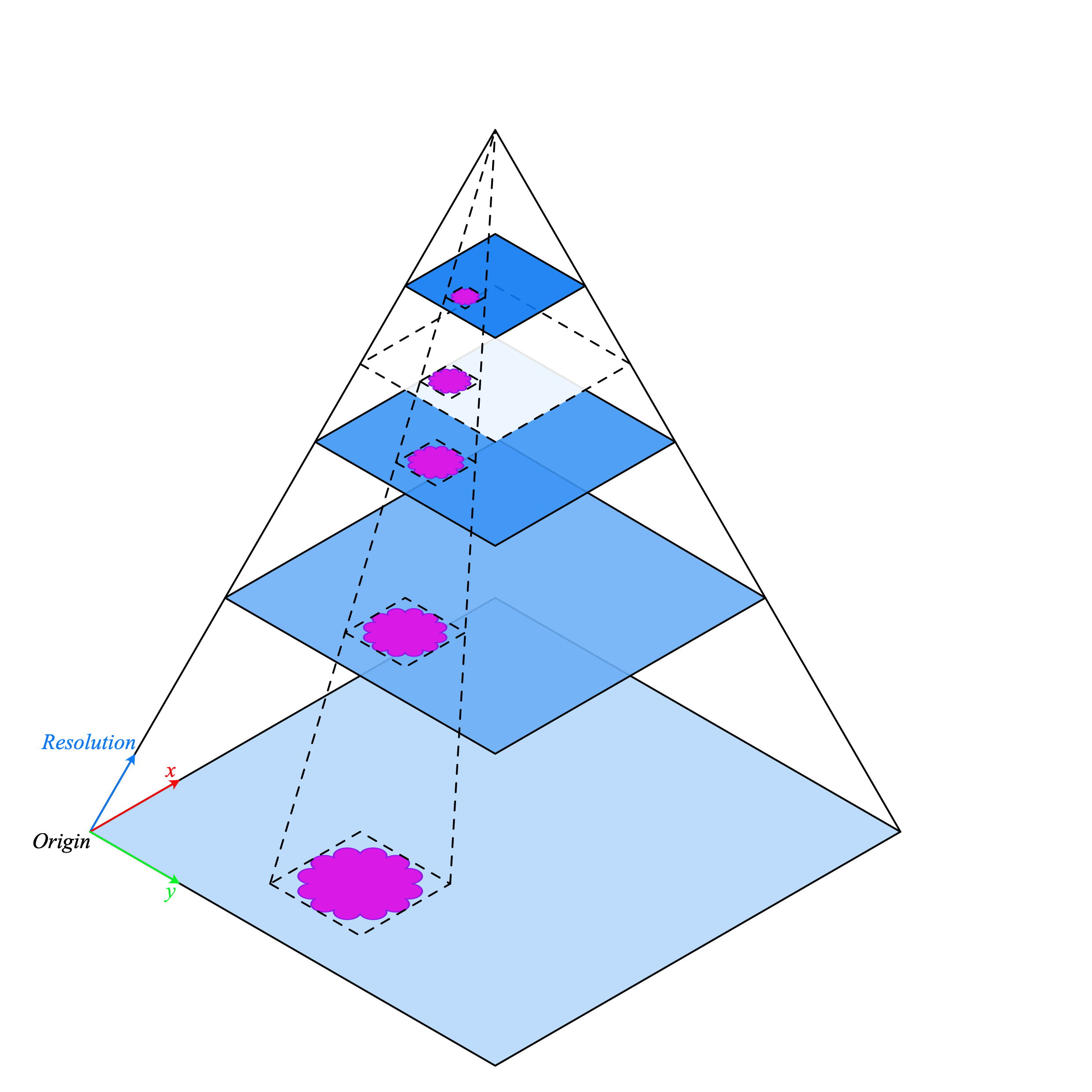
This is because the bounds are in the baseline (level 0) reference frame. Therefore, varying the resolution does not change what is visible within the output image.
If the WSI does not have a resolution layer corresponding exactly to the requested resolution (shown above in white with a dashed outline), a larger resolution is downscaled to achieve the correct requested output resolution.
If the requested resolution is higher than the baseline (maximum resultion of the image), then bicubic interpolation is applied to the output image.
- read_rect(location, size, resolution=0, units='level', interpolation='optimise', pad_mode='constant', pad_constant_values=0, coord_space='baseline', **kwargs)[source]¶
Read a region of the whole slide image at a location and size.
Location is in terms of the baseline image (level 0 / maximum resolution), and size is the output image size.
Reads can be performed at different resolutions by supplying a pair of arguments for the resolution and the units of resolution. If metadata does not specify mpp or objective_power then baseline units should be selected with resolution 1.0
The field of view varies with resolution. For a fixed field of view see
read_bounds().- Parameters:
location (IntPair) – (x, y) tuple giving the top left pixel in the baseline (level 0) reference frame.
size (IntPair) – (width, height) tuple giving the desired output image size.
resolution (Resolution) – Resolution at which to read the image, default = 0. Either a single number or a sequence of two numbers for x and y are valid. This value is in terms of the corresponding units. For example: resolution=0.5 and units=”mpp” will read the slide at 0.5 microns per-pixel, and resolution=3, units=”level” will read at level at pyramid level / resolution layer 3.
units (Units) – The units of resolution, default = “level”. Supported units are: microns per pixel (mpp), objective power (power), pyramid / resolution level (level), pixels per baseline pixel (baseline).
interpolation (str) – Method to use when resampling the output image. Possible values are “linear”, “cubic”, “lanczos”, “area”, and “optimise”. Defaults to ‘optimise’ which will use cubic interpolation for upscaling and area interpolation for downscaling to avoid moiré patterns.
pad_mode (str) – Method to use when padding at the edges of the image. Defaults to ‘constant’. See
numpy.pad()for available modes.pad_constant_values (int, tuple(int)) – Constant values to use when padding with constant pad mode. Passed to the
numpy.pad()constant_values argument. Default is 0.coord_space (str) – Defaults to “baseline”. This is a flag to indicate if the input bounds is in the baseline coordinate system (“baseline”) or is in the requested resolution system (“resolution”).
**kwargs (dict) – Extra key-word arguments for reader specific parameters. Currently only used by VirtualWSIReader. See class docstrings for more information.
self (WSIReader)
- Returns:
Array of size MxNx3 M=size[0], N=size[1]
- Return type:
Example
>>> from tiatoolbox.wsicore.wsireader import WSIReader >>> # Load a WSI image >>> wsi = WSIReader.open(input_img="./CMU-1.ndpi") >>> location = (0, 0) >>> size = (256, 256) >>> # Read a region at level 0 (baseline / full resolution) >>> img = wsi.read_rect(location, size) >>> # Read a region at 0.5 microns per pixel (mpp) >>> img = wsi.read_rect(location, size, 0.5, "mpp") >>> # This could also be written more verbosely as follows >>> img = wsi.read_rect( ... location, ... size, ... resolution=(0.5, 0.5), ... units="mpp", ... )
Note: The field of view varies with resolution when using
read_rect().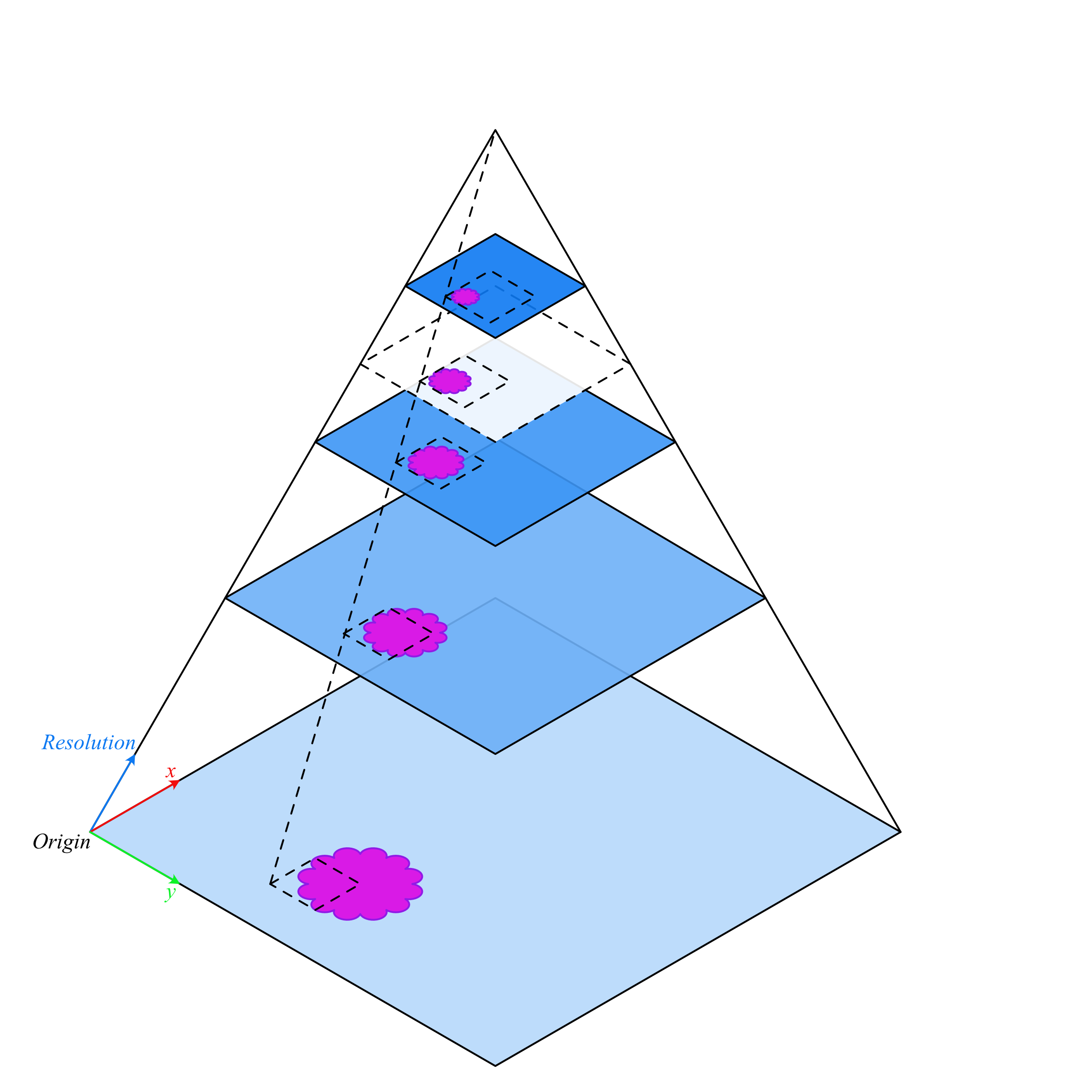
As the location is in the baseline reference frame but the size (width and height) is the output image size, the field of view therefore changes as resolution changes.
If the WSI does not have a resolution layer corresponding exactly to the requested resolution (shown above in white with a dashed outline), a larger resolution is downscaled to achieve the correct requested output resolution.
If the requested resolution is higher than the baseline (maximum resultion of the image), then bicubic interpolation is applied to the output image.
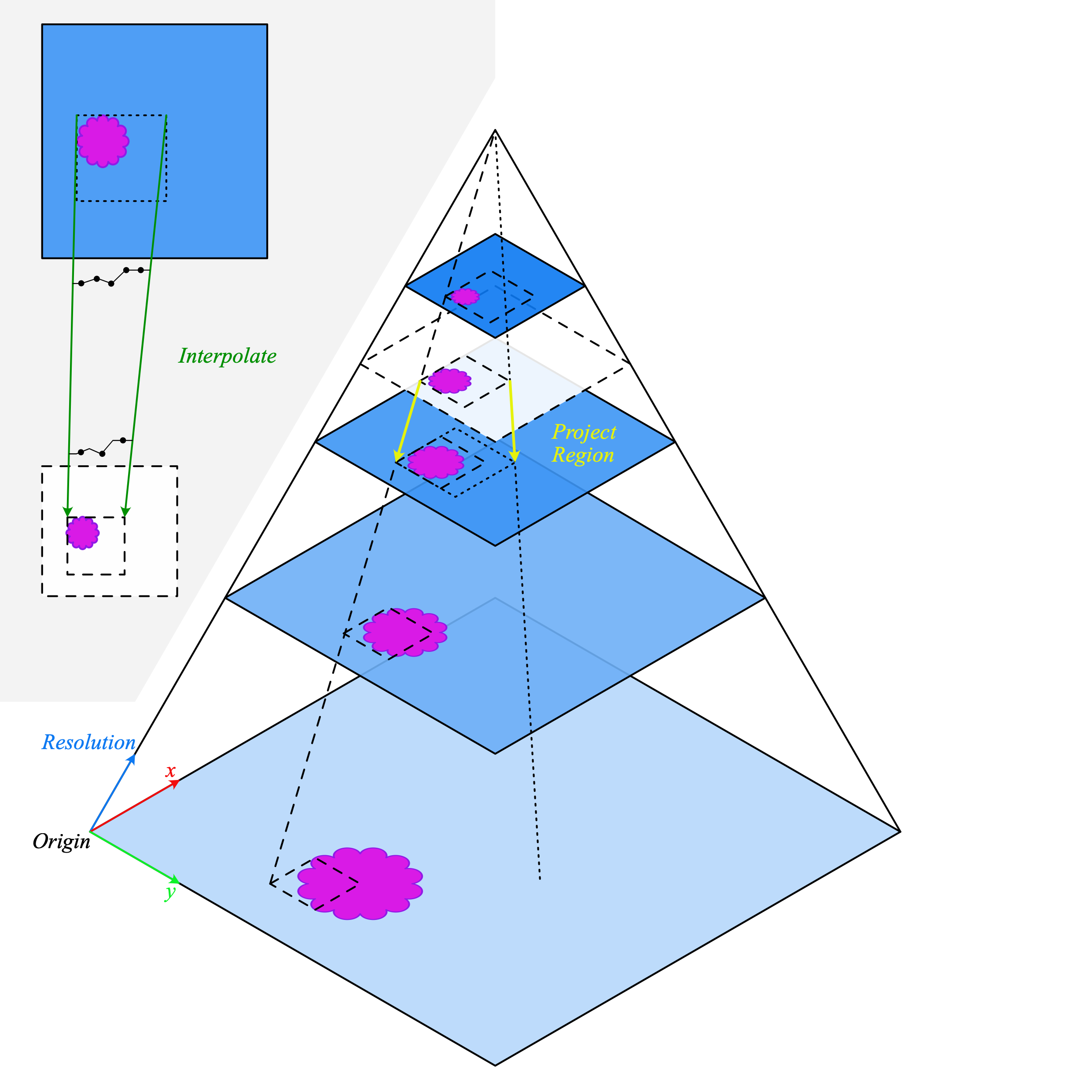
When reading between the levels stored in the WSI, the coordinates of the requested region are projected to the next highest resolution. This resolution is then decoded and downsampled to produce the desired output. This is a major source of variability in the time take to perform a read operation. Reads which require reading a large region before downsampling will be significantly slower than reading at a fixed level.
Examples
>>> from tiatoolbox.wsicore.wsireader import WSIReader >>> # Load a WSI image >>> wsi = WSIReader.open(input_img="./CMU-1.ndpi") >>> location = (0, 0) >>> size = (256, 256) >>> # The resolution can be different in x and y, e.g. >>> img = wsi.read_rect( ... location, ... size, ... resolution=(0.5, 0.75), ... units="mpp", ... ) >>> # Several units can be used including: objective power, >>> # microns per pixel, pyramid/resolution level, and >>> # fraction of baseline. >>> # E.g. Read a region at an objective power of 10x >>> img = wsi.read_rect( ... location, ... size, ... resolution=10, ... units="power", ... ) >>> # Read a region at pyramid / resolution level 1 >>> img = wsi.read_rect( ... location, ... size, ... resolution=1, ... units="level", ... ) >>> # Read at a fractional level, this will linearly >>> # interpolate the downsampling factor between levels. >>> # E.g. if levels 0 and 1 have a downsampling of 1x and >>> # 2x of baseline, then level 0.5 will correspond to a >>> # downsampling factor 1.5x of baseline. >>> img = wsi.read_rect( ... location, ... size, ... resolution=0.5, ... units="level", ... ) >>> # Read a region at half of the full / baseline >>> # resolution. >>> img = wsi.read_rect( ... location, ... size, ... resolution=0.5, ... units="baseline", ... ) >>> # Read at a higher resolution than the baseline >>> # (interpolation applied to output) >>> img = wsi.read_rect( ... location, ... size, ... resolution=1.25, ... units="baseline", ... ) >>> # Assuming the image has a native mpp of 0.5, >>> # interpolation will be applied here. >>> img = wsi.read_rect( ... location, ... size, ... resolution=0.25, ... units="mpp", ... )
- read_region(location, level, size)[source]¶
Read a region of the whole slide image (OpenSlide format args).
This function is to help with writing code which is backwards compatible with OpenSlide. As such, it has the same arguments.
This internally calls
read_rect()which should be implemented by anyWSIReadersubclass. Therefore, some WSI formats which are not supported by OpenSlide, such as Omnyx JP2 files, may also be readable with the same syntax.- Parameters:
- Returns:
Array of size MxNx3.
- Return type:
- save_tiles(output_dir='tiles', tile_objective_value=20, tile_read_size=(5000, 5000), tile_format='.jpg', *, verbose=False)[source]¶
Generate image tiles from whole slide images.
- Parameters:
output_dir (str or
Path) – Output directory to save the tiles.tile_objective_value (int) – Objective value at which tile is generated, default = 20
tile_read_size (tuple(int)) – Tile (width, height), default = (5000, 5000).
tile_format (str) – File format to save image tiles, defaults = “.jpg”.
verbose (bool) – Print output, default=False
self (WSIReader)
- Return type:
None
Examples
>>> from tiatoolbox.wsicore.wsireader import WSIReader >>> wsi = WSIReader.open(input_img="./CMU-1.ndpi") >>> wsi.save_tiles(output_dir='./dev_test', ... tile_objective_value=10, ... tile_read_size=(2000, 2000))
>>> from tiatoolbox.wsicore.wsireader import WSIReader >>> wsi = WSIReader.open(input_img="./CMU-1.ndpi") >>> slide_param = wsi.info
- slide_dimensions(resolution, units, precision=3)[source]¶
Return the size of WSI at requested resolution.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
Size of the WSI in (width, height).
- Return type:
Examples
>>> from tiatoolbox.wsicore.wsireader import WSIReader >>> wsi = WSIReader.open(input_img="./CMU-1.ndpi") >>> slide_shape = wsi.slide_dimensions(0.55, 'mpp')
- slide_thumbnail(resolution=1.25, units='power')[source]¶
Read the whole slide image thumbnail (1.25x by default).
For more information on resolution and units see
read_rect()- Parameters:
resolution (Resolution) – Resolution to read thumbnail at, default = 1.25 (objective power)
units (Units) – Resolution units, default=”power”.
self (WSIReader)
- Returns:
Thumbnail image.
- Return type:
Examples
>>> from tiatoolbox.wsicore.wsireader import WSIReader >>> wsi = WSIReader.open(input_img="./CMU-1.ndpi") >>> slide_thumbnail = wsi.slide_thumbnail()
- tissue_mask(method='otsu', resolution=1.25, units='power', **masker_kwargs)[source]¶
Create a tissue mask and wrap it in a VirtualWSIReader.
For the morphological method, mpp is used for calculating the scale of the morphological operations. If no mpp is available, objective power is used instead to estimate a good scale. This can be overridden with a custom size, via passing a kernel_size key-word argument in masker_kwargs, see
tissuemask.MorphologicalMaskerfor more.- Parameters:
method (str) – Method to use for creating the mask. Defaults to ‘otsu’. Methods are: otsu, morphological.
resolution (float) – Resolution to produce the mask at. Defaults to 1.25.
units (Units) – Units of resolution. Defaults to “power”.
**masker_kwargs – Extra kwargs passed to the masker class.
self (WSIReader)
- Return type:
- static verify_supported_wsi(input_path)[source]¶
Verify that an input image is supported.
- Parameters:
input_path (
Path) – Input path to WSI.- Raises:
FileNotSupportedError – If the input image is not supported.
- Return type:
None